A financial audit is an independent examination of an organization's financial records, statements, and transactions to ensure accuracy, compliance with accounting standards, and reliability. The purpose of a financial audit is to provide an objective assessment of an organization's financial position, performance, and financial reporting. During a financial audit, auditors review various financial documents, such as balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements, and supporting records. They examine the organization's accounting policies, procedures, and internal controls to assess their effectiveness in preventing errors, fraud, or misstatements.
Types of Audit
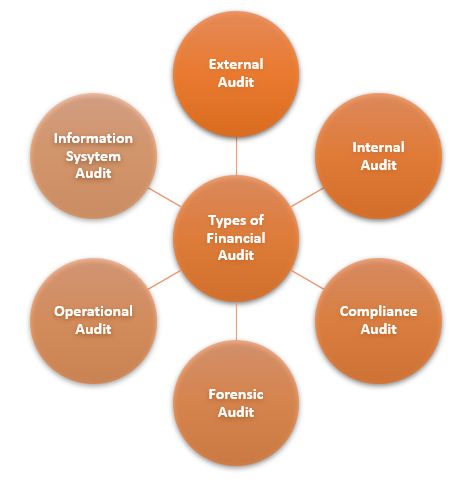
There are several types of financial audits that can be conducted based on the specific objectives and scope of the audit. Here are a few common types of financial audits:
- External Audit: External audits by independent firms or CPAs evaluate financial statements' fairness and accuracy, often mandated by regulatory bodies and stakeholders. For example, a publicly traded company may undergo an external audit to ensure compliance with financial reporting standards and provide assurance to investors.
- Internal Audit: Internal audits evaluate organizational controls, risk management, and operational efficiency, assessing compliance, identifying areas for improvement, and providing management recommendations. For instance, a manufacturing company may conduct an internal audit to assess inventory controls, production processes, and cost management.
- Compliance Audit: Compliance audit assesses an organization's adherence to laws, regulations, and industry standards. An example of a compliance audit is when a financial institution undergoes an audit to verify compliance with anti-money laundering regulations or consumer protection laws.
- Forensic Audit: A forensic audit investigates financial irregularities, fraud, or misconduct within an organization using specialized techniques to gather evidence, analyze transactions, and identify fraudulent activities. It is often conducted when suspicions of fraud, such as embezzlement or financial statement manipulation, are raised.
- Operational Audit: Operational audit assesses an organization's processes, procedures, efficiency, effectiveness, and risk management, aiming to identify improvement opportunities and optimize performance. For example, Retail company undergoes operational audit to assess inventory management, supply chain processes, and customer service practices.
- Information System Audit: An information systems audit evaluates an organization's IT infrastructure, data security, and controls. It assesses financial data reliability, integrity, governance practices, and effectiveness of controls. The audit may also ensure data privacy compliance or cybersecurity measures.
Need of Financial Audit
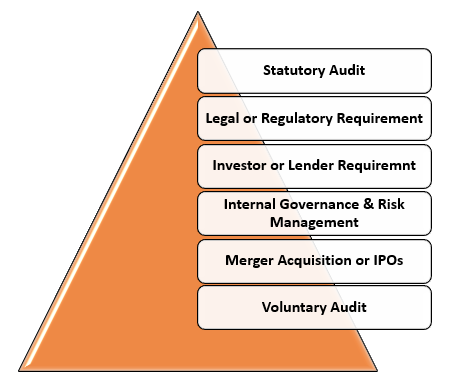
Financial audits are conducted in various situations. Here are some scenarios where financial audit are conducted:
- Statutory Audit: Jurisdictions mandate financial audits for specific organizations, like publicly traded companies, to ensure compliance and shareholder interests.
- Legal or regulatory Requirement: Industries like banking, insurance, and healthcare require financial audits to ensure compliance with specific regulations.
- Investor or Lender requirement: Financial audits may be required by investors, venture capitalists, and lenders for funding or credit, reducing information asymmetry.
- Internal Governance & Risk Management: Internal financial audits evaluate internal controls, identify risk, and improve financial management practices in organizations for governance and risk management.
- Merger Acquisition or IPOs: Financial audits assess company's position, performance, and risks in business transactions, enabling potential buyers, investors, and underwriters.
- Voluntary audit: Organizations may conduct voluntary financial audits to improve credibility, trust, transparency, attract investors, and align with industry best practices.
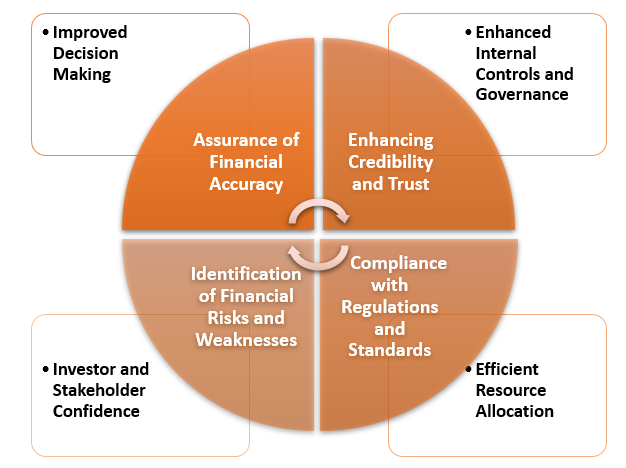
Benefits of Financial Audit
Financial audits can provide several benefits to an organization. Here are some ways in which financial audits can benefit an organization:
- Assurance of Financial Accuracy: A financial audit assesses an organization's financial statements, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and compliance with accounting standards, providing confidence to management, shareholders, investors, and stakeholders.
- Enhancing Credibility and Trust: Financial audits demonstrate transparency, accountability, and build trust with stakeholders, enhancing an organization's reputation and credibility.
- Identification of Financial Risks and Weaknesses: Auditors review internal controls, systems, and processes to identify weaknesses, gaps, and potential risks, enabling management to take corrective measures and strengthen controls.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: Financial audits ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and accounting standards, especially for publicly traded companies. They help identify and rectify noncompliance issues, preventing penalties, fines, and damage to reputation.
- Improved Decision Making: Audits provide reliable financial information for informed decisions, cost-saving opportunities, investment evaluation, and strategic goals setting.
- Enhanced Internal Controls and Governance: Financial audits evaluate an organization's internal controls and governance processes, offering recommendations for strengthening controls, improving efficiency, and mitigating risks.
- Investor and Stakeholder Confidence: Regular financial audits boost investor and stakeholder confidence in organizations, assessing financial health, performance, and risk profile, attracting potential investors and partners.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Financial audits evaluate organizations' financial position, identify strengths, inefficiencies, and unnecessary expenditures, enabling resource allocation and optimization.