Human Resource Management (HRM) refers to the strategic and comprehensive approach taken by organizations to manage and maximize the effectiveness of their human resources. It involves the activities, policies, and practices aimed at attracting, developing, motivating, and retaining a talented and diverse workforce.
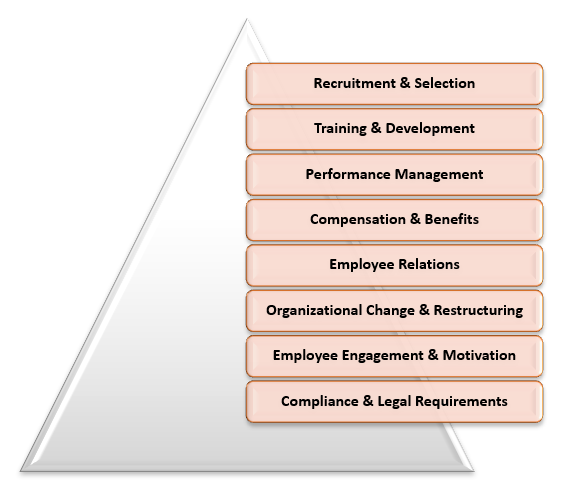
Functions of Human Resource Management
The primary objective of HRM is to align the human resources of an organization with its strategic goals and objectives. It encompasses a wide range of functions and responsibilities, including:
- Recruitment and Selection: HRM handles job requirements, candidate selection, interviews, and filling organizational positions.
- Training & Development: HRM implements training programs, career development, and succession planning to improve employees' skills, knowledge, and job performance.
- Performance Management: HRM implements performance evaluation systems for employee evaluation, feedback, goal setting, and improvement.
- Compensation & Benefits: HRM manages compensation and benefits programs, ensuring fair, competitive compensation to attract and retain top talent.
- Employee Relations: HRM manages employee relations through policies, procedures, positive work environment, grievance handling.
- Employee Engagement & Motivation: HRM fosters an engaging work environment through initiatives like recognition, teamwork, and well-being.
- Organizational change & restructuring: HRM manages organizational change processes, facilitating restructuring, workforce transitions, and addressing employee concerns.
- Compliance & legal Requirements: HRM ensures organization adheres to labor laws, regulations, and industry standards through employee records and contracts.
Functions of HRM
Steps of Human Resource Management
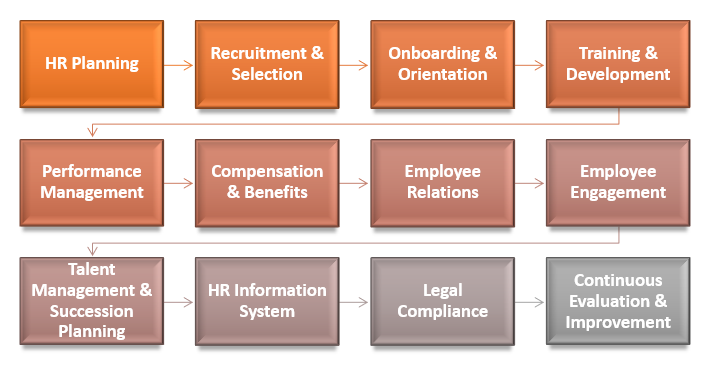
HRM involves steps to effectively manage an organization's human resources:
- Human Resource Planning: Assessing and identifying organizational human resource needs aligns with strategic objectives, forecasting workforce requirements, analyzing skills gaps, and developing strategies.
- Recruitment & Selection: HRM attracts qualified candidates through job descriptions, advertising, sourcing, screening, interviews, and selecting the best-fit candidates.
- Onboarding & Orientation: HRM assists candidates in smooth integration by offering orientation, introducing culture, policies, and resources.
- Training & Development: HRM develops and implements training programs to improve employees' skills, knowledge, and capabilities.
- Performance Management: HRM implements performance management systems to assess employee performance, set goals, provide feedback, and recognize high performers.
- Compensation & Benefits: HRM oversees compensation, benefits, payroll, employee benefits, and legal compliance for organizations.
- Employee relations: HRM promotes positive employee relations through policies, procedures, communication, and conflict management.
- Employee Engagement: HRM promotes employee engagement, satisfaction through positive work environment, teamwork, recognition, and work-life balance.
- Talent Management & Succession Planning: HRM identifies, develops high-potential employees through talent assessment, career planning, and succession planning.
- HR Information System: HRM uses technology to manage employee data, automate processes, generate reports, and ensure data privacy and security.
- Legal Compliance: HRM ensures compliance with labor laws, employment regulations, and legal requirements, ensuring documentation, equal employment opportunity, and up-to-date legislation.
- Continuous Evaluation & Improvement: HRM continuously evaluates practices and processes, gathering feedback, conducting surveys, analyzing metrics, and implementing changes to improve effectiveness.
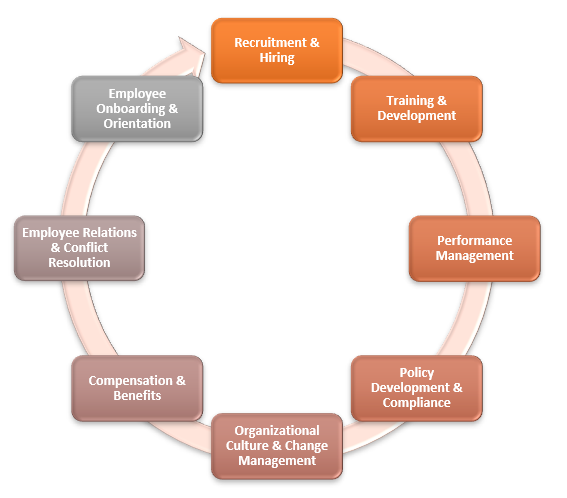
Need of HR
Human Resource departments are appointed to address various issues within the organization such as:
- Recruitment & Hiring: HR manages job vacancies, hiring, and onboarding, including job descriptions, advertising, and interviews.
- Employee Onboarding & Orientation: HR ensures seamless employee integration by providing paperwork, explaining policies, conducting orientations, and providing necessary resources.
- Employee Relations & Conflict Resolution: HR manages employee relations, promoting a positive work environment, resolving disputes, and ensuring fair treatment.
- Performance Management: HR designs and implements performance management systems, collaborating with managers to set goals, evaluate, and develop improvement plans.
- Training & Development: HR identifies training needs, designs programs, and supports employee development, enhancing performance.
- Compensation & Benefits: HR oversees employee compensation, benefits, payroll, compliance, and employee benefits.
- Policy development & Compliance: HR creates policies and procedures governing employee behavior, work expectations, and compliance with employment laws.
- Organizational Culture & Change Management: HR crucial for culture development, values alignment, diversity promotion, and effective change management.
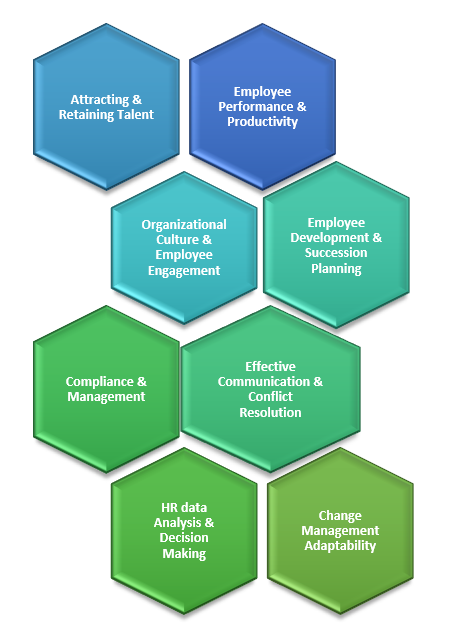
Benefits of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) can bring several benefits to an organization. Here are some ways HRM can positively impact an organization:
- Attracting & Retaining Talent: HRM practices attract top talent through a well-defined recruitment process, competitive compensation, and a positive work environment, while retaining talented employees through career development opportunities and recognition programs.
- Employee Performance & Productivity: HRM practices attract top talent through a well-defined recruitment process, competitive compensation, and a positive work environment, while retaining talented employees through career development opportunities and recognition programs.
- Organizational Culture and Employee Engagement: HRM fosters a positive organizational culture, promoting transparency, open communication, teamwork, and well-being, enhancing employee satisfaction, loyalty, and productivity.
- Employee Development & Succession Planning: HRM develops employees' skills and potential through training, career development, and succession planning, reducing external hiring dependency and promoting long-term organizational stability.
- Compliance and Risk Management: HRM ensures organization compliance with employment laws, regulations, and ethical standards, mitigating risks and protecting from lawsuits and reputation damage.
- Effective Communication & Conflict Resolution: HRM promotes effective communication, employee feedback, fair grievances, and conflict resolution, fostering a positive work environment and improving teamwork and cohesion.
- Change Management & Adaptability: HRM supports organizational change initiatives, helps employees navigate transitions, manages processes, communicates, addresses concerns, and fosters adaptability for effective response to market dynamics.
- HR Data Analysis and Decision-Making: HRM utilizes data analytics to analyze workforce metrics, identify trends, anticipate challenges, and develop strategies, improving organizational strategy and decision-making.